Drug Testing
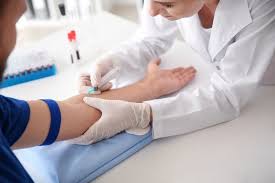
Drug testing is a methodical procedure created to identify the presence or absence of illegal drugs or their metabolites in a person's body. It functions as a crucial tool in a variety of settings, including police enforcement, sports leagues, and healthcare facilities. The procedure usually entails gathering biological samples, such as urine, blood, saliva, or hair, which are then examined in specialized laboratories utilizing cutting-edge methods and machinery. Promoting safety and security is one of the main goals of drug testing, especially in workplaces where impairment from drug use can pose serious concerns. Employers frequently set up drug testing programs to maintain a drug-free workplace, protect their workers, and assure productivity and efficiency.
Companies can reduce workplace accidents, improve overall performance, and deter employee drug usage by identifying those who may be impaired by drugs. To maintain fairness and integrity during competitive events, sports organizations also use drug testing. The use of performance-enhancing drugs, such as anabolic steroids or stimulants, which can give athletes unfair advantages and undermine the spirit of sportsmanship, is discouraged by routine testing of athletes. Governing bodies can enforce anti-doping laws, safeguard athletes' health, and uphold the values of fair play by administering drug tests. Overall, drug testing is a valuable tool that supports safety, justice, and well-being in various contexts. Employers, sports leagues, law enforcement, and healthcare practitioners may make informed judgments, put effective interventions into place, and contribute to the general welfare of people and society by identifying drug use and misuse.


Comments
Post a Comment